





Validate your AI or Platform Idea in 40 Engineering hours. Talk to our Expert →
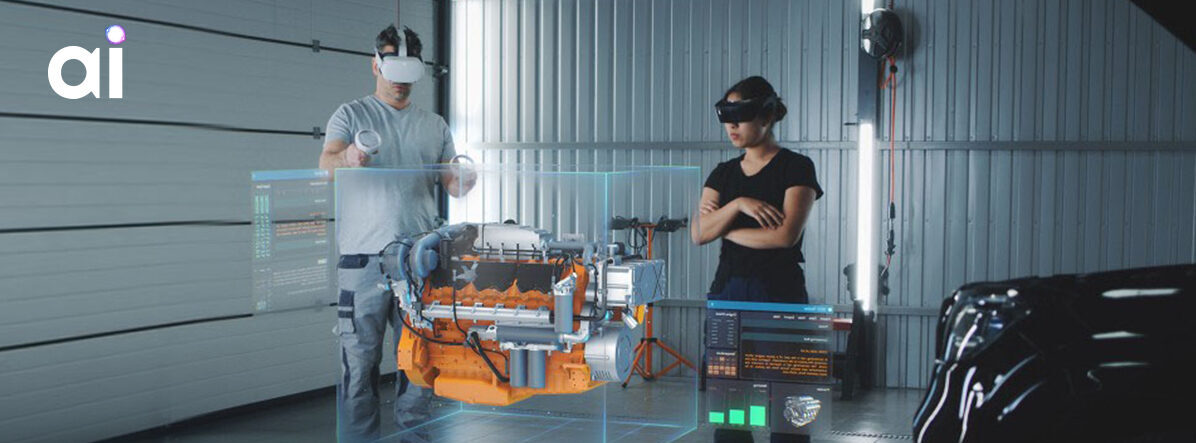

Extended Reality (XR) is a term used to describe immersive technologies that blend physical and digital environments. XR enhances how users perceive and interact with digital information by embedding it within spatial, contextual and interactive experiences.
Rather than consuming content through flat screens, XR enables users to experience digital elements in three dimensions, interact with virtual objects, and participate in simulated scenarios that reflect real-world conditions. This shift from passive consumption to active participation is what differentiates XR from traditional digital technologies.
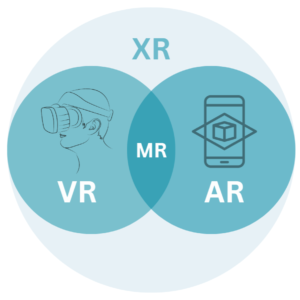
XR is not a single technology. Instead, it represents a spectrum that includes Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). Each of these technologies offers a different level of immersion and interaction, allowing organizations to select the approach that best fits their objectives and constraints.
Virtual Reality places users inside a fully simulated digital environment. Using VR headsets and controllers, users are visually and audibly immersed in a virtual world that blocks out the physical surroundings. VR is commonly used for training, simulation, and experiential learning, where complete focus and controlled environments are required.
Augmented Reality overlays digital information onto the real world. Users continue to see their physical environment, enhanced with contextual digital elements such as instructions, visuals, or data. AR is often used for on-the-job guidance, maintenance support, and real-time information delivery.
Mixed Reality combines elements of both VR and AR. Digital objects not only appear in the real world but also interact with physical surroundings in a meaningful way. MR is particularly useful for complex visualization, collaborative work, and advanced training scenarios.
Together, VR, AR, and MR form the XR ecosystem, enabling a range of experiences from fully immersive simulations to subtle digital enhancements of real-world tasks

XR solutions are built through a structured development pipeline that transforms real-world environments and processes into immersive, interactive experiences. Unlike traditional software, XR development begins with spatial understanding and 3D content creation before moving into simulation and deployment.
The process starts with converting physical assets such as equipment, workspaces, or products into accurate 3D models using CAD data, scans, or digital design tools. These models form the foundation for XR experiences.
Next, workflows and interactions are designed to define how users move, interact, and perform tasks within the environment, enabling realistic process simulation without physical risk.
These experiences are then implemented using XR platforms and engines that handle rendering, physics, and spatial behaviour, ensuring realistic and responsive environments.
Once developed, experiences are optimized and deployed across VR, AR, and MR devices. Throughout the lifecycle, analytics capture performance and interaction data, enabling continuous improvement and allowing XR to scale as a reliable, enterprise-ready capability.
XR is being applied across industries to address real operational challenges.
The most successful XR implementations focus on repeatable, scalable use cases that integrate into existing workflows rather than one-off demonstrations.
Despite its potential, XR adoption presents challenges. Organizations often struggle with scaling content beyond pilots, managing change across teams, aligning with IT and security requirements, keeping experiences updated, and measuring real impact.
These challenges are best addressed by treating XR as a long-term capability rather than a standalone project. Modular content design enables updates and reuse. Early involvement of training, operations, and IT teams ensures alignment. Analytics-driven iteration allows continuous improvement based on real usage data.
Organizations that succeed with XR focus on governance, ownership and integration into everyday processes. Over time, XR becomes part of how teams learn, operate, and improve not an isolated initiative.
Extended Reality is evolving from an emerging technology into a strategic enterprise capability. Its true value lies not in immersive visuals alone, but in its ability to support learning, decision-making, and continuous improvement at scale.
As XR technologies continue to mature, organizations that prioritize realism, adaptability, and data-driven insights will be best positioned to unlock sustained value. When implemented with the right mindset, XR becomes an integral part of modern digital operations.